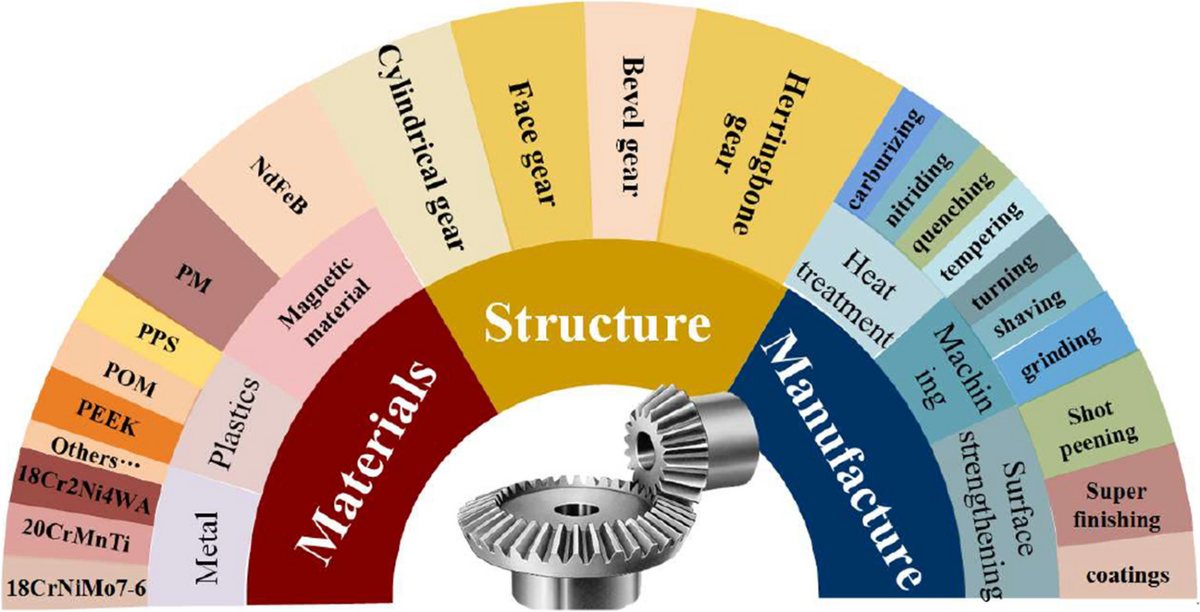
Gears are produced from a variety of materials depending on their application, required strength, durability, and other factors. Here are some
common materials used for gear production:
1. Steel
Carbon Steel: Widely used due to its strength and hardness. Commonly used grades include 1045 and 1060.
Alloy Steel: Offers enhanced properties such as improved toughness, strength, and resistance to wear. Examples include 4140 and 4340 alloy
steels.
Stainless Steel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and is used in environments where corrosion is a significant concern. Examples include
304 and 316 stainless steels.
2. Cast Iron
Grey Cast Iron: Offers good machinability and wear resistance, commonly used in heavy machinery.
Ductile Cast Iron: Provides better strength and toughness compared to grey cast iron, used in applications requiring higher durability.
3. Non-Ferrous Alloys
Bronze: An alloy of copper, tin, and sometimes other elements, bronze is used for gears requiring good wear resistance and low friction.
Commonly used in marine and industrial applications.
Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc, brass gears offer good corrosion resistance and machinability, used in applications where moderate strength is
sufficient.
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum gears are used in applications where weight reduction is important, such as in
aerospace and automotive industries.
4. Plastics
Nylon: Provides good wear resistance, low friction, and is lightweight. Commonly used in applications requiring quieter operation and lower loads.
Acetal (Delrin): Offers high strength, stiffness, and good dimensional stability. Used in precision gears and applications where low friction is
needed.
Polycarbonate: Known for its impact resistance and transparency, used in specific applications where these properties are beneficial.
5. Composites
Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics: Combine the benefits of plastics with added strength and durability from fiberglass reinforcement, used in
lightweight and corrosion-resistant applications.
Carbon Fiber Composites: Provide high strength-to-weight ratios and are used in high-performance applications such as aerospace and racing.
6. Specialty Materials
Titanium: Offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, used in high-performance and aerospace applications.
Beryllium Copper: Known for its high strength, non-magnetic properties, and corrosion resistance, used in specialized applications such as
precision instruments and marine environments.
Gear Material:
| Type | Standard | Grade Number | Application |
| Metal Gear | GB/T5216, DIN, JIS G4052, SAE, EN & etc.. | 20CrMnTiH, 20CrH~40CrH, 20CrNiMo, 20CrMoH~42CrMoH, CrMnMoH, CrNiMoH, 20CrNi3H, MnBH, SCr415H~SCr440H, SCM415H~SCM440H, 8620H~8627H, 4120H~4145H, 4320H, 4340H, 5137H, 15NiMo4, 15CrNi6, 16CrNi4, 19CrNi5, 17CrNiMo6, 34CrNiMo6, 25CrMo4, 42CrMo4, 49CrMo4, 30CrMoV9, 16MnCr5 | Aviation, Gearbox, Reducer, Automobile, Agriculture, Construction Machine, Machinery Industry and etc.. |
| Plastic Gear | GB, DIN, JIS, SAE, EN & etc.. | POM, PA, TPEE, PC, PEEK, PPO, PVDF, PE, UHMWPE, TPEE | Gearbox, Reducer, Automobile, Agriculture, Construction Machine, Machinery Industry and etc.. Machinery Industry |
Considerations for Material Selection:
Load Requirements:
High loads and stresses typically require stronger materials like steel or alloy steel.
Operating Environment:
Corrosive environments necessitate materials like stainless steel or bronze.
Weight:
Applications requiring lightweight components may use aluminum or composite materials.
Cost:
Budget constraints can influence the choice of material, balancing performance and cost.
Machinability:
The ease of manufacturing and machining can impact material choice, especially for complex gear designs.
Friction and Wear:
Materials with low friction and good wear resistance, such as plastics or bronze, are chosen for applications needing smooth
and durable operation.
Post time: Jul-05-2024