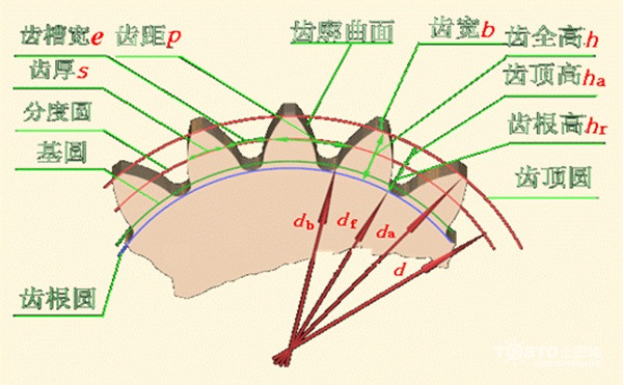
1. Number of teeth Z The total number of teeth of a gear.
2, modulus m The product of the tooth distance and the number of teeth is equal to the circumference of the dividing circle, that is, pz= πd,
where z is a natural number and π is an irrational number. In order for d to be rational, the condition that p/π is rational is called the modulus. That is: m=p/π
3, the diameter of the indexing circle d the tooth size of the gear are determined based on this circle d=mz copy full text 24, the diameter of the top circle d. And the diameter of the root circle de full screen reading from the calculation formula of the crest height and the root height, the calculation formula of the crest circle diameter and the root circle diameter can be derived:
d.=d+2h.=mz+2m=m(z+2)
The greater the modulus of the wheel, the higher and thicker the teeth, if the number of teeth of the
gear is certain, the larger the radial size of the wheel. Modular series standards are formulated according to the requirements of design, manufacturing and inspection. For gears with non-straight teeth, the modulus has the difference between the normal modulus mn, the end modulus ms and the axial modulus mx, which are based on the ratio of their respective pitch (normal pitch, end pitch and axial pitch) to PI, and are also in millimeters. For bevel gear, the module has the big end module me, the average module mm and the small end module m1. For the tool, there is the corresponding tool modulus mo and so on. Standard modules are widely used. In the metric gear drive, worm drive, synchronous gear belt drive and ratchet, gear coupling, spline and other parts, the standard modulus is the most basic parameter. It plays a basic parameter role in the design, manufacture and maintenance of the above parts
1)The modulus indicates the size of the teeth. The R-module is the ratio of the pitch of the dividing circle to the PI (π), expressed in millimeters (mm). In addition to modules, we have Diametral pitch (CP) and DP (Diametral pitch) to describe the size of the teeth. The diametral pitch is the length of the dividing arc between equivalent points on two adjacent teeth.
2) What is “index circle diameter”? The index circle diameter is the reference diameter of the gear. The two main factors that determine the size of the gear are the modulus and the number of teeth, and the diameter of the dividing circle is equal to the product of the number of teeth and the modulus (end face).
3) What is a “pressure Angle”? The acute Angle between the radial line at the intersection of the tooth shape and the tooth shape tangent of the point is called the pressure Angle of the reference circle. Generally speaking, the pressure Angle refers to the pressure Angle of the indexing circle. The most commonly used pressure Angle is 20°; however, gears with pressure angles of 14.5 °, 15°, 17.5 °, and 22.5° are also used.
4) What is the difference between single-head and double-head worm? The number of spiral teeth of the worm is called the “number of heads”, which is equivalent to the number of teeth of the gear. The more heads there are, the greater the lead Angle.
5) How to distinguish R (right-handed)? L (left) Gear shaft vertical ground flat gear tooth tilt to the right is the right gear, tilt to the left is the left gear.
6) What is the difference between M (modulus) and CP(pitch)? CP (Circular pitch) is the circular pitch of the teeth on the index circle. The unit is the same as the modulus in millimeters. CP divided by PI (π) yields M (modulus). The relationship between M (modulus) and CP is shown as follows. M (modulus) =CP/π (PI) Both are units of tooth size. (The dividing circumference = n d=zpd=z p/ l/PI is called the modulus

7) What is a “backlash”? The gap between the tooth surfaces of a pair of gears when they are engaged. Backlash is a necessary parameter for the smooth operation of gear meshing. 8) What is the difference between bending strength and tooth surface strength? Generally, the strength of gears should be considered from two aspects: bending and tooth surface strength. Bending strength is the strength of the tooth that transmits power to resist the tooth breaking at the root due to the action of bending force. The tooth surface strength is the frictional strength of the tooth surface during repeated contact of the meshed tooth. 9) In the bending strength and tooth surface strength, what strength is used as the basis for selecting the gear? In general, both bending and tooth surface strength need to be discussed. However, when selecting gears that are used less frequently, hand gears, and low-speed meshing gears, there are cases where only bending strength is selected. Ultimately, it’s up to the designer to decide.
Post time: Oct-31-2024